Services
Using the latest technology in a fully accredited hospital facility
Why choose Goa Lasik?
- Availability of LASIK, PRK and LASIK treatments
- The ability to treat numbers ranging from +1 to +8 and -1 to -12.
- Availability of advanced topography guided ablation & customized ablation.
- Availability of
total range of refractive solutions- namely Lasik. Icl &Ipcl , Clear lens exchange( Refractive lens exchange)
Our Hospital has unique features like
- Eco friendly Green building
- The whole building is positively pressurised with FILTERED fresh air, Rich in oxygen and Dust free
- Public zones, Private Zones, Sterile and Semi sterile areas clearly demarkated
- Modular operation theaters- 3 in numbers with HEPA filters and laminar air flow
The evergreen destination of Goa is a holiday maker’s paradise
Beautiful blue beaches, golden sands, flora
The State Of The Art Equipments
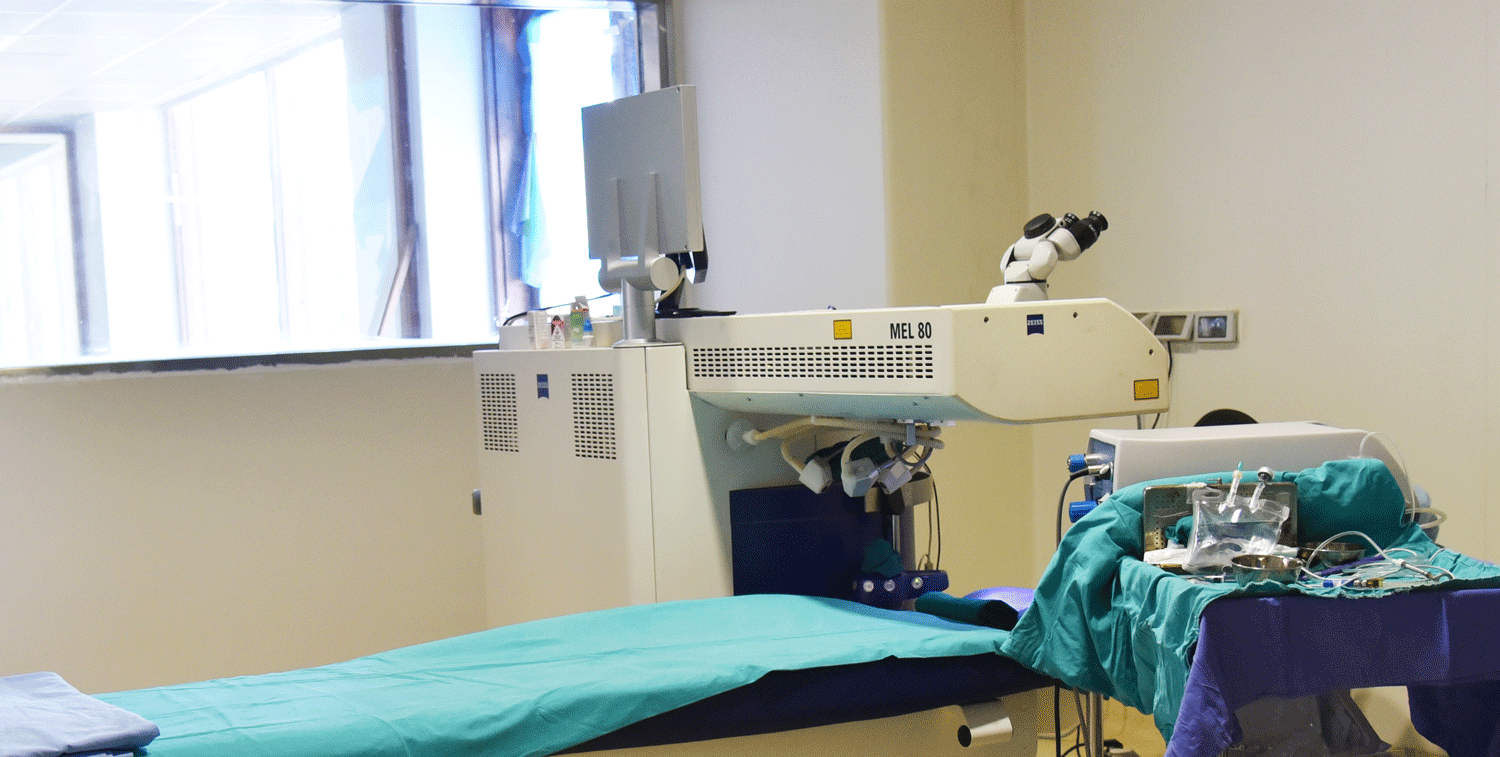
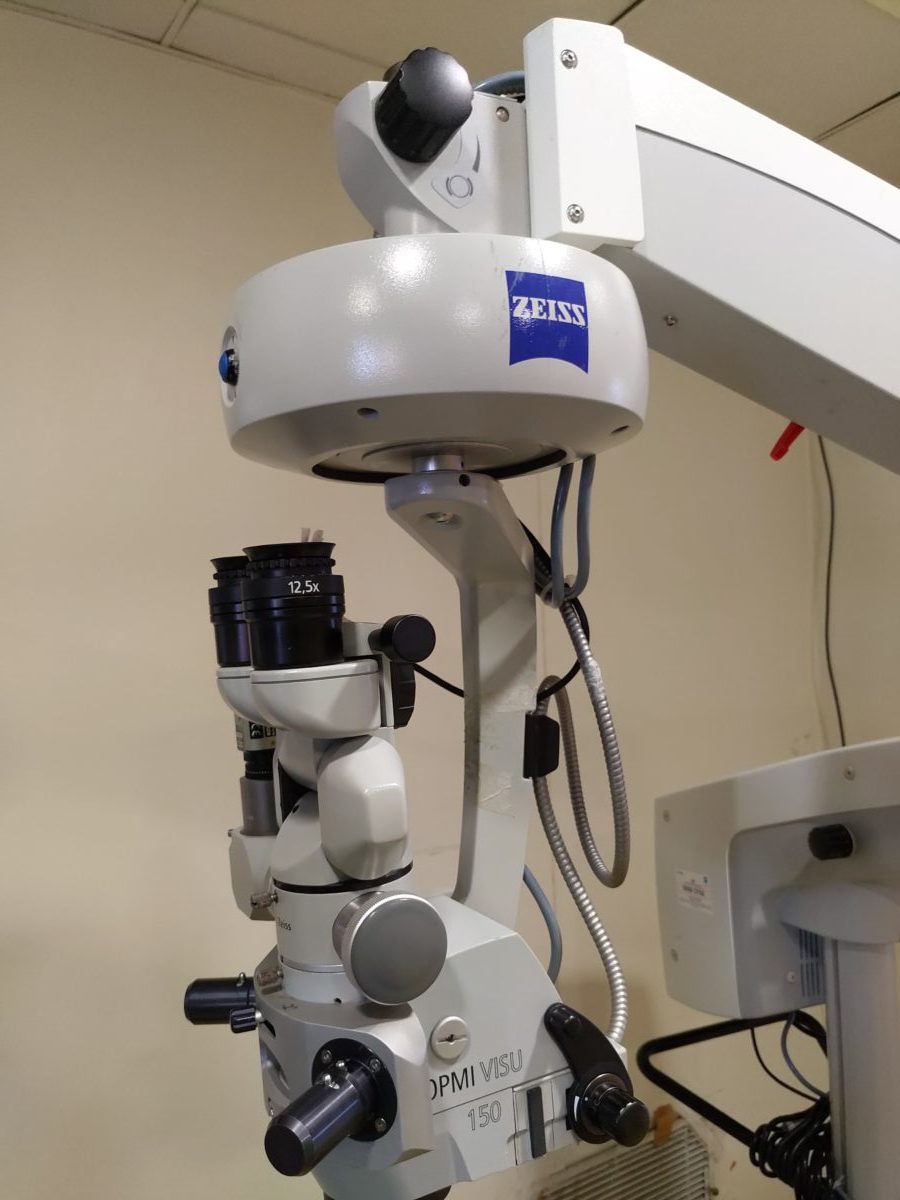
Zesis – Excimer Laser
GOA LASIK
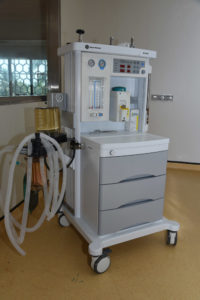
GE Datex – Ohmeda Anasthesia work station
ETO Sterilizer
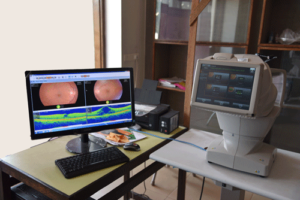
INFINITY Vision Systems
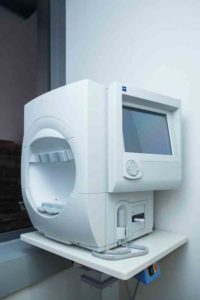
Humphrey Field Analyzer 3 Model 840
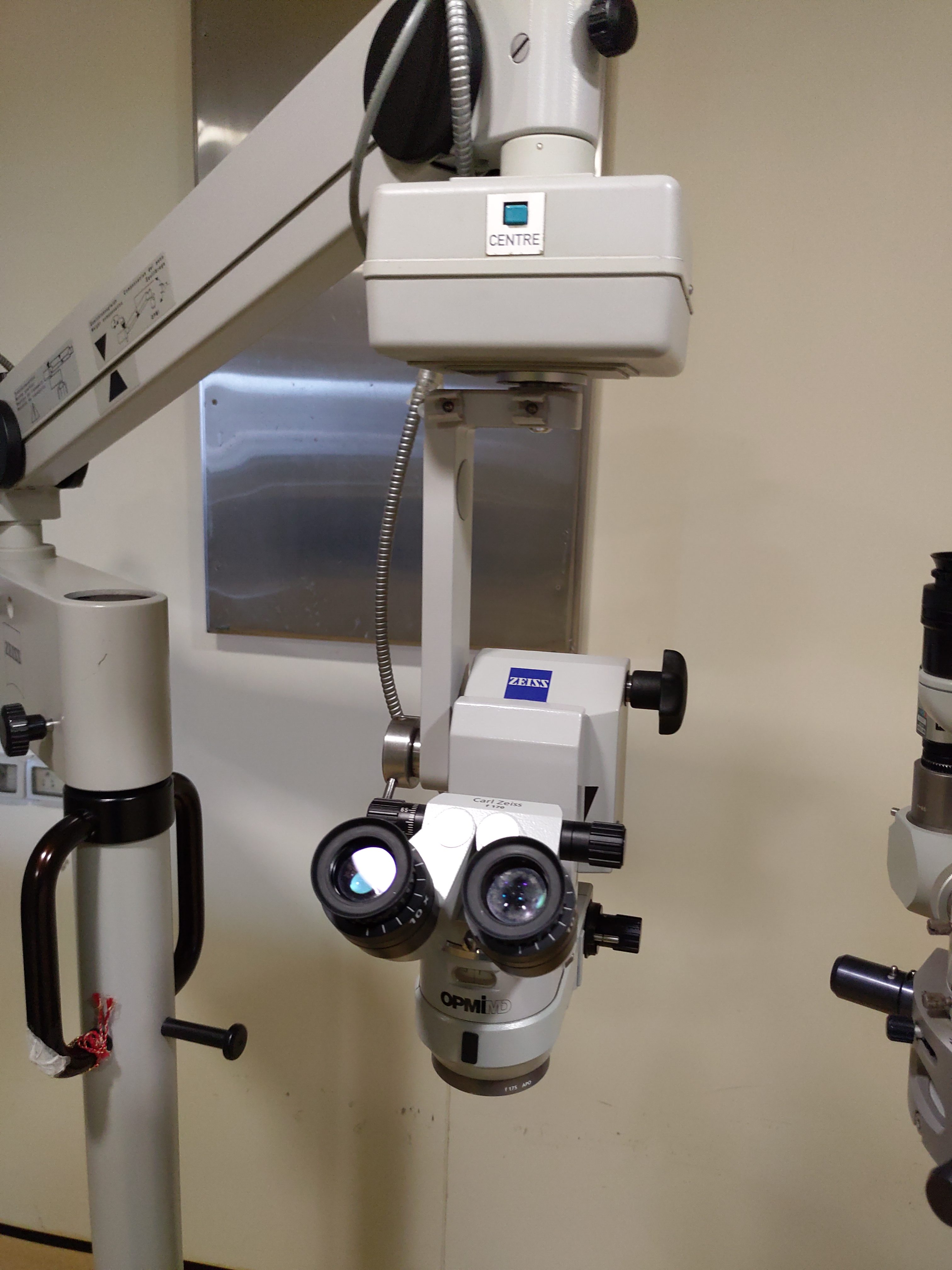
Zesis Operation Microscopes
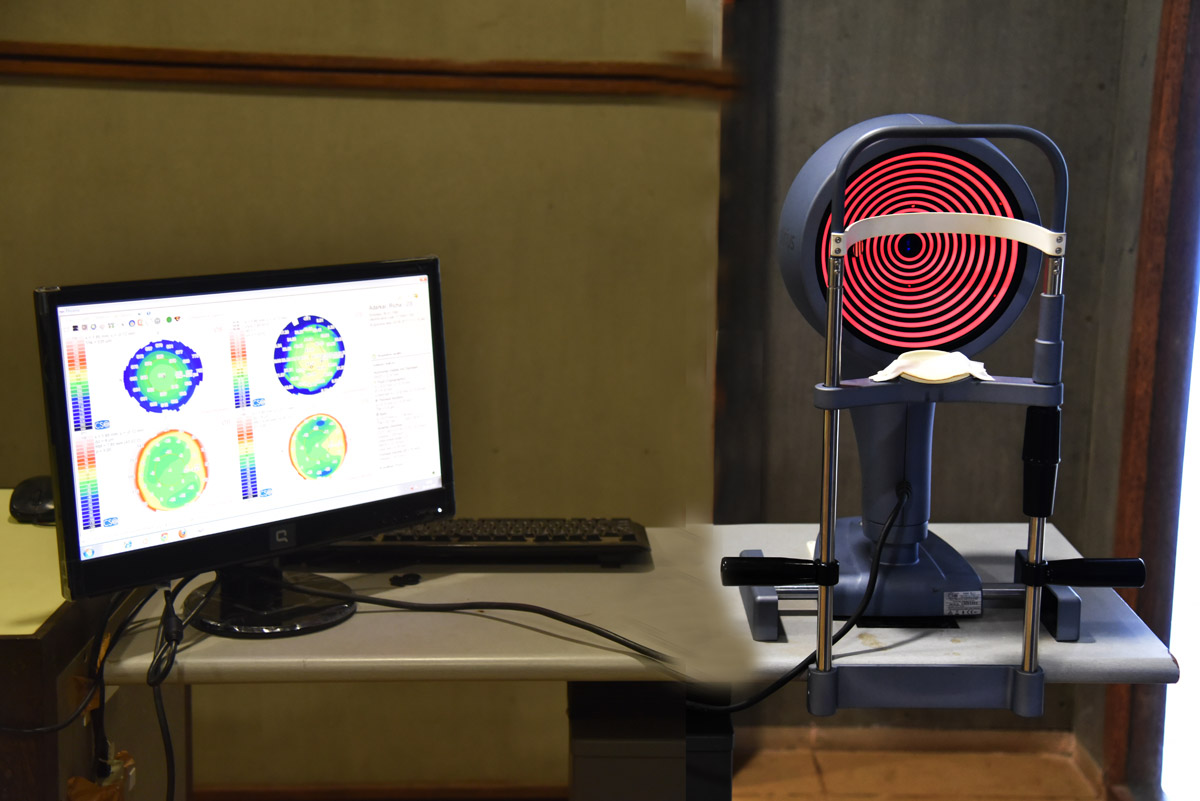
(for Dry Eye)
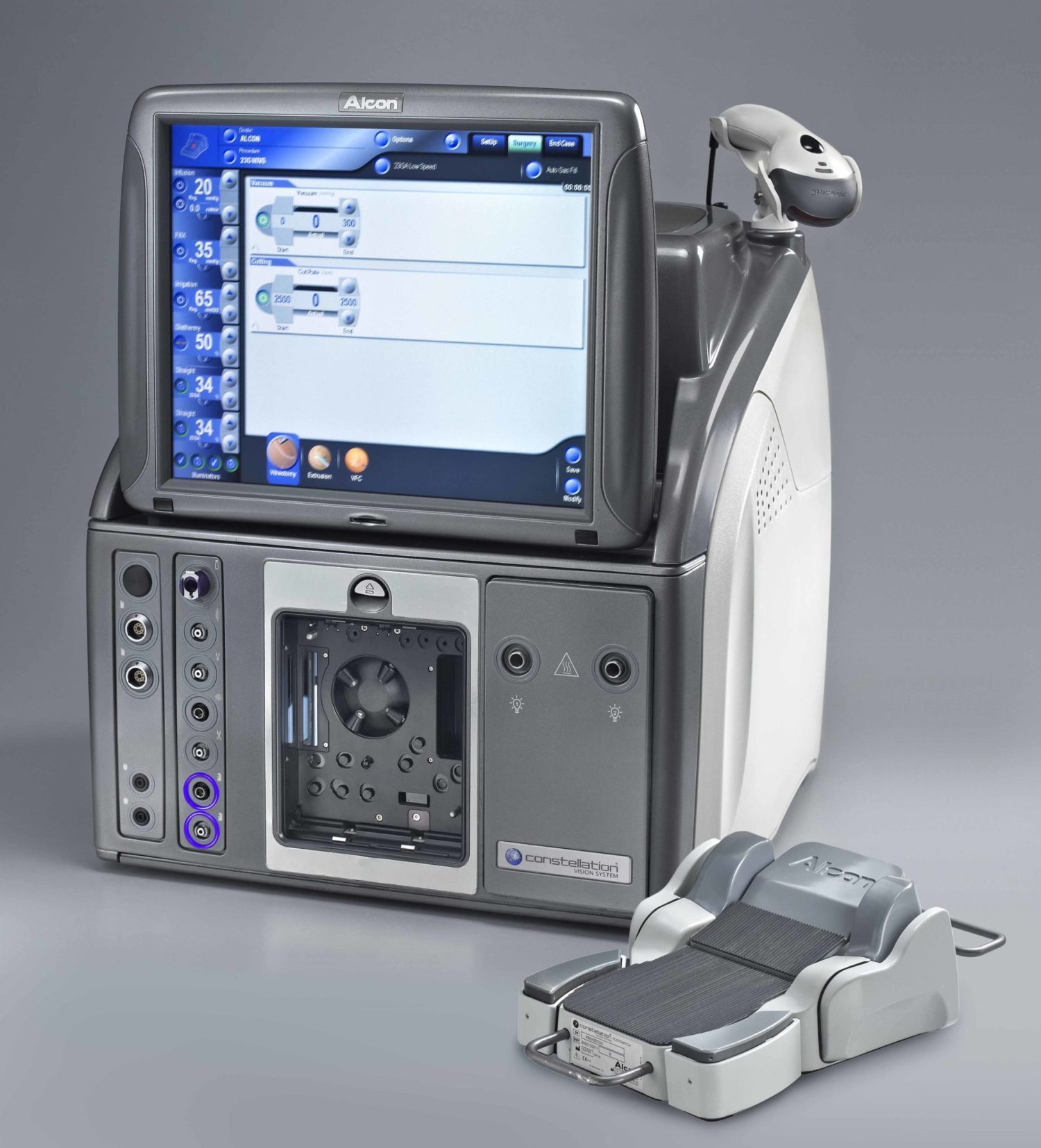
ALCON Constellation Vision System
3D Maestro OCT (TOPCON)
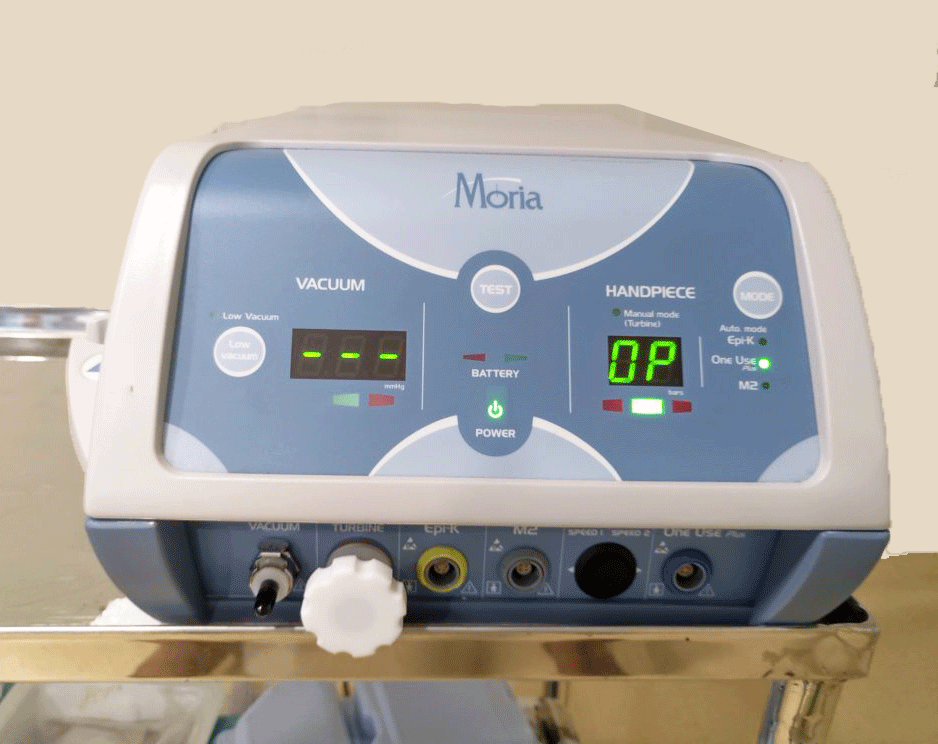
Moria BSK MK
Wasca Analyzer, USA
Sirius Schemflg Tomography
Besides these high speed sterilizers, routine diagnostic equipments such as chair units, refraction units, Ultrasonography A, slit lamps, direct and indirect Ophthalmoscopes, Lensomer, Laser/Indirect lenses (Volk, Occular Heine, etc) are from leading multi-national brands. We will strive hard and hope to add more sophisticated equipments periodically in our pursuit towards state of the art high quality super specialized eye care to all – that is comparable to the best in the world.
Specialized In
- Medical Retina
- Squint Clinic
- Refractive surgery
- Lens replacement surgery
- Surgical Retina
- Pediatric
- Glaucoma
- Cataract
- The Dry Eye
- Diabetic Eye
- Cornea Services
Diagnosis & treatment of retina vasular conditions such as Diabetic Retropathy (DR), age related macular degeneration (AMD) with cnvm, central Retinal vein occlusion (CRVO).
Treatment includes Retinal Photocoagulation (Retinal Lasers), Intravitreal injections of Bevacizumals (Avastain), Ranibizumab (Lucentis/Accentrix), Aflipercept (Eyelea), Ozurdex.
Squints can be cured by glasses and eye exercises and in certain cases surgery must be done at the earliest to rectify the misalignment.
When both the eyes of a person are not in alignment with each other it is known as squint or strabismus. Nearly 40% patients with squint can be cured by spectacles and/or eye exercises. However, a large majority require an operation. Squint operations are very safe and should be done at the earliest. Generally if the eyes are not aligned for more than 6 months in a child, irreversible damage to the three dimensional vision occurs, which is only partly reversible. Squint surgeries are performed successfully even in 4 month old children. If surgery is required it should be done in most cases within six months after the squint is noticed to avoid any irreversible damage to three dimensional vision.
What is squint (strabismus)?
Squint is a misalignment of the two eyes where both eyes are not looking in the same direction. This misalignment may be constant or may be present throughout the day or it may appear occasionally and the rest of the time the eyes may be straight; this is called as intermittent squint.
What causes squint?
The exact cause of squint is not known. Six muscles control the movement of each eye (see picture). Each of these muscles acts along with its counterpart in the other eye to keep both the eyes aligned properly. A loss of coordination between the muscles of the two eyes leads to misalignment. Sometimes a refractive error like hypermetropia (far sightedness) or an eye muscle paralysis may lead to deviation of the eye. Poor vision in an eye because of some other eye disease like cataract etc. may also cause the eye to deviate. Therefore it is important in all cases of squint, especially in children, to have a thorough eye checkup to rule out any other cause of loss of vision.
When to see a doctor?
Make an appointment for an eye exam if you notice any changes in your vision. If you develop sudden vision changes, such as double vision or flashes of light, sudden eye pain, or sudden headache, see your doctor right away.
Center for Refractive & Therapeutic surgical procedures.
The following excimer related procedures are commonly performed in this hospital.
- LASIK (MEL80-ZEISS) with SBK 90 (MORIA)
- PRK
- PTK (for corneal opacities, recurrent erosions, none healing abrasions)
- KERATOCONUS – For
Diagonsis and treatment- SIRIUS system (Topography)
- C3R (Collagen
cross linking ) - C3R plus (C3R combined with
topoguided PRK in KC - Phakic
IOLs (ICL, IPCL)
Lens Replacement surgery:
Carma Services
Lens replacement surgery is normally used to refer to one of three similar types of treatments: Refractive Lens Exchange (RLE), Implantable Contact Lenses (ICL) and Cataract Surgery, with each having alternative names and acronyms so it can be a little confusing.
BEST CANDIDATES
hyperopia, presbyopia, ineligibility for LASIK or phakic IOL
- Procedure time:about 15 minutes per eye
- Typical results:clear vision at all distances without glasses or contact lenses
- Recovery time:a few days to several weeks
Types Of Lens Replacement Surgery
- Refractive Lens Exchange (RLE)
In general, when people talk about lens replacement surgery they are referring to some type of Refractive Lens Exchange (RLE), which is also known as Refractive Lens Replacement, Clear Lens Exchange (CLE) or Clear Lens Surgery. This is a treatment for patients suffering from presbyopia (long-sightedness normally occurring in middle and old age), hyperopia (farsightedness where objects nearby are not seen as clearly as objects in the distance) or those with a considerably thin cornea.
- Cataract Surgery
Cataract surgery involves the same procedure as the refractive lens surgery described above, except that the lens that is removed is not clear but cloudy due to
- Implantable Contact Lenses (ICL)
This type of lens surgery involves implanting contact lenses rather than removing and replacing the natural lens which occurs in lens replacement surgery. This new phakic intraocular lens is placed on top of the natural lens and behind the iris (the exact positioning will depend on the lens chosen). As the natural lens is not removed this procedure can be reversed at a later date.
Is There Anything I Should Avoid After Surgery?
- To help make sure your recovery period is a successful one, there are a number of things you’ll need to avoid post-surgery to ensure this, including:
- Avoid swimming for a week after your surgery
- Refrain from contact sports for a month – non-contact sports (e.g. jogging or going to the gym) can be resumed the day after your surgery, but you should try not to overexert yourself as high blood pressure can hamper your recovery
- Avoid touching your eyes or letting any smoke, dust or sweat get into them for at least a month to help prevent any infections
- To reduce your risk of eye fatigue try not to watch television for too long and refrain from extended periods of computer work
- Avoid driving for a few days after your surgery (your surgeon will be able to advise when it’s safe for you to resume this)
Surgeries
The most common indications for a vitrectomy include:
- Diabetic vitreous hemorrhage
- Retinal detachment
- Epiretinal membrane
- Macular hole
- Proliferative vitreoretinopathy
- Endophthalmitis
- Intraocular foreign body removal
- Retrieval of
lens nucleus following complicated cataract surgery
Advanced surgical treatment of
Pediatric eyecare
A child should go for an eye checkup if the following symptoms are noticeable
- Crossed eyes.
- Keeps
object close to his eyes. - Not being able to see the blackboard at school.
- Things looking blurry or funny.
- Feeling an itching, burning or scratchy sensation in the eyes.
- Injury to the eye.
- One or both the parents wear glasses.
What are the Common Eye Diseases in children?
- Refractive errors
- Lazy eye disease
- Eye injuries
- Squinting of eyes
- Watering from the eyes
- Eye allergies
What is Lazy Eye Disease?
This is a common eye disease affecting nearly 5-10% of children. In this
What do I do if the child’s eyes go red?
- Do not put any eye drop especially the ones with Steroids.
Glaucoma is an eye disease that causes loss of sight by damaging a part of the eye called the optic nerve. This nerve sends information from your eyes to your brain. When glaucoma damages your optic nerve, you begin to lose patches of vision, usually side vision (peripheral vision). Over time, glaucoma may also damage straight ahead (central) vision. You may not notice a loss of side vision until you have lost a great deal of your
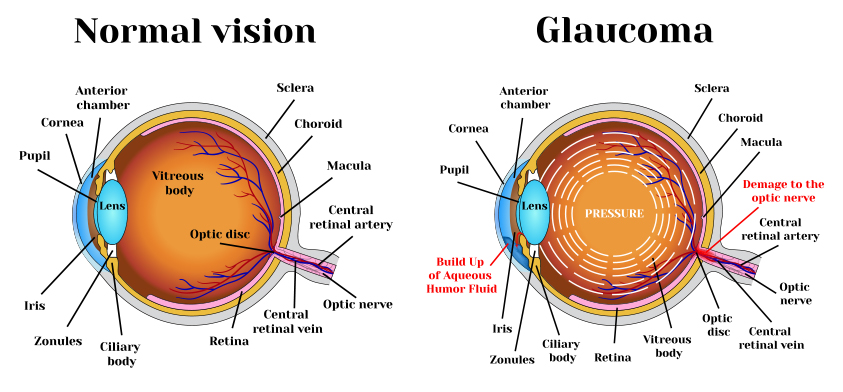
What are the three major signs that a person may have glaucoma?
- Optic nerve damage
- Vision loss (visual field loss)
- Increased eye pressure (elevated intraocular pressure)
Who is at Risk for Glaucoma?
These risk factors may increase your chance of having glaucoma:
- Age: The older you are, the greater your risk
- Race: African-Americans have glaucoma four to five times more often than others.
- African -Americans: are also likely to have glaucoma at a younger age
- Family
history : If you have a parent, brother or sister with glaucoma, you are more likely to get glaucoma too. If you have glaucoma, your family members should get complete eye exams.
Medical history: Medical history: Diabetes, previous eye injuries, eye surgery or long-term steroid use anywhere in the body can increase your risk of glaucoma. Anyone can get glaucoma it affects one in 200 people until the age of 50. The rate increases to one in 10
- over the age of 80.
What is Cataract?
The common symptoms of Cataract include:
- A painless blurring vision
- Glare or light sensitivity
- Poor night vision
- Double vision in one eye
- Needing brighter light to red
- Fading yellowing of colors
What causes Cataract?
How cataract treated?
Surgery is the only way a cataract can be removed. Surgery consists of removal of cataract & replacement with an
Modern cataract surgery performed at My Eye
Cataract surgery is performed under topical anesthesia i.e. few drops of anesthesia – NO
- The preferred surgical technique used in phaco emulsification ( cold phaco ) with foldable Intra Ocular Lens
implantation . - We at present use Infiniti Vision Systems from Alcon Incl.
USA for Advanced Phaco. - Cataract surgery lasts for about 15 – 20 minutes. You can choose from
variety of IOLs. We use all types of IOls ranging from non-foldable to foldable and the latestpresbyopia correcting IOLs ( Restor Acrysof Multifocal from Alcon, USA, Tecnis Multifocal Resume from AMO, USA) which reduces the spectacle dependence afteroperation . - Drapes, knives – used by us are disposable and imported from USA/Japan.
WHAT IS THE DRY EYE ?
The Dry Eye is a tear film disorder due to reduced production or excessive evaporation of tears, which causes damages to the exposed ocular surface and is associated to a sensation of eye discomfort.
Excessive evaporation of tears (cause of 86% of Dry Eye cases) is induced by the obstruction or malfunction of the Meibomian glands that are located in the eyelids, and are responsible for producing the tears lipid layer.
When not working properly, the Meibomian gland does not produce enough oily components for the tear film, which consequently evaporates quicker. Insufficient or absent lipid layer, can cause tear evaporation up to 16 times faster.
- Over 300 million people worldwide suffer for the Dry Eye Syndrome.
- In Italy it involves 26% of adult population, but this syndrome mainly affects women over 40 years old (50%) and those in menopause (90%).
Risk factors
- Allergic conjunctivitis
- Hormonal imbalances – Menopause
- Use and abuse of eye cosmetics
- Use of contact lenses.
- Chronic blepharitis
- Age (especially after age 50)
- Prolonged use of video terminals
- Prolonged use of systemic drugs (i.e antihistamines, etc)
- Air pollution
Diagonsis
Dry eye diagonsis should always be made Opthalmologist with reliable tests, thus avoiding self diagonsis and treatment “over the counter”. The Opthalmologist will consisder a number of parameters and correct the therapy for each specific case.
The cure
There are several solutions for the dry eye problem, going from artificaltears (eyedrops) to a new generation of therapeutic treatments.
Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetic Mellitus is a condition which impairs the body’s ability to use and store sugar.
This can
which consists of:
- Temporary blurring of vision – with each attack of hyperglycemia (increased blood sugar level)
- Cataract –
early clouding of the human crystalline lens, needing cataract surgery by phacoemulsification. - Glaucoma a condition of increased intraocular pressure needing lifeline medication/surgery.
- Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) resulting from damage to the blood vessels of the retina. (It is the commonest and the most
sight threatening complication of Diabetes).
How common is DR
- Nearly 50-80% of all diabetics get DR sometimes in their lifetime.
- The longer someone has diabetes, the more likely that he/she will get DR.
- Poor control of blood sugar will cause early onset of DR.
How is the Treatment?
Timely treatment by Laser Photocoagulation of the retina is the only method to arrest the progress of the disease, in addition to good control of blood sugar, Blood pressure and smoking.
What can you do to protect your vision?
- Successful treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy depends not only on early detection through medical eye examination and treatment by an
opthalmologist but also on thepatients attitude and attention to medications and diet. It is important to remember that Diabetic Retinopathy may be present without any symptoms. - Early detection of Diabetic Retinopathy is the best protection against loss of vision.
- It is a silent killer of sight.
- Blindness caused by Diabetic Retinopathy is
irresversible in natural (i.e. sight lost is lost forever) - Hence, early diagnostic by periodic dilated eye checking (eye year) is a must.
- Laser Photocoagulation of the retina is the only proved treatment for control.
- Stop smoking, Good control of Diabetes and Blood Pressure is a must.